Wireless
L4S in Wi-Fi: A Path to Seamless Interactive Experiences

Key Points
- Broadband service providers are beginning to implement L4S functionality in their networks. The technology enables applications to achieve low latency and high efficiency, ultimately helping deliver enhanced and more reliable user experiences.
- CableLabs worked with the Wireless Broadband Alliance to develop a set of guidelines for equipment suppliers to use when implementing L4S in their Wi-Fi products.
- Wi-Fi networks are frequently a point of congestion in end-to-end networks, creating a need for L4S support in those networks.
Modern networks deliver impressive speeds — often reaching gigabits per second — yet they still suffer from unpredictable delays that can disrupt interactive applications. Whether it’s video conferencing, cloud gaming or remote collaboration, these inconsistencies can lead to frustrating user experiences. As network operators strive to enhance reliability and responsiveness, a more effective solution is needed.
To address this need, the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) — an organization responsible for developing open internet standards — has specified the Low Latency, Low Loss and Scalable (L4S) throughput architecture. L4S enables applications to implement a new mechanism to ensure that they are sending their data as fast as the network can support, but no faster. The result is efficient capacity usage with minimal queuing delay and low packet loss.
This shift to a more comprehensive quality of service (QoS) model is essential for delivering smooth and uninterrupted performance across a wide range of services, from gaming and video streaming to cloud computing and augmented reality.
What Is L4S?
The power of L4S stems from new congestion control algorithms that adapt to new fine-grain notifications of congestion at the IP layer across various network elements along an end-to-end (E2E) path. While L4S can be deployed on each element of the network, its most significant impact is at points of congestion, also referred to as network bottlenecks — where the rate of incoming packets can exceed the departure rate.
The cable industry already adopted support for L4S, as part of the Low Latency DOCSIS® 3.1 specifications (and it carries forward into DOCSIS 4.0 gear as well). Operators are beginning to enable this functionality in their networks, and more are expected to do so over the coming months. That said, the broadband access network segment is only one potential bottleneck. There are others on the E2E path.
The Need for L4S in Wi-Fi Networks
Wi-Fi networks, in particular, require L4S support as they are frequently a point of congestion in E2E networks. Indeed, although Wi-Fi networks often advertise their maximum capacity that is greater than the broadband access connection, actual performance is significantly influenced by factors such as the distance between clients and the access point (AP), as well as the number of APs and clients operating on the same channel. This need for L4S support is even more critical given that a substantial portion of internet traffic is transmitted over Wi-Fi.
WBA L4S Implementation Guidelines and NS3 Simulator
Wi-Fi presents unique challenges for L4S implementation compared to wired technologies such as DOCSIS® networks. While wired networks primarily see only buffering delays, Wi-Fi additionally introduces media access delays, which can be significant in congested environments. To tackle these challenges, CableLabs worked within the End-to-End QoS Working Group of the Wireless Broadband Alliance (WBA) to produce a set of guidelines to implement L4S in current Wi-Fi products.
The guidelines cover:
- An overview of L4S technology, explaining its mechanics and benefits.
- The importance of L4S support in Wi-Fi equipment for improving E2E application performance.
- Implementation strategies for Wi-Fi equipment suppliers to enable L4S functionality in their products.
- Simulation and test results demonstrating the advantages of L4S in real-world scenarios
The simulation results are based on a Wi-Fi NS3 model developed by CableLabs, designed to evaluate L4S performance in Wi-Fi networks. The model is open-source and available to industry and research players to support L4S deployment and assess its impact on various use cases. In addition, CableLabs provided field test data that were conducted with a Nokia AP.
The Future of L4S in Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi equipment suppliers today can leverage the L4S Implementation Guidelines to develop support on their existing platforms (e.g. Wi-Fi 7 devices). Several proposals from industry leaders, including CableLabs, aim to incorporate L4S support into the 802.11 Wi-Fi standard, ensuring native support for L4S across future Wi-Fi generations.
In addition, as the ecosystem matures, CableLabs will continue refining the NS3 model to expand its applicability to more scenarios and use cases. This ongoing effort is being advanced in collaboration with the WBA E2E QoS working group.
L4S is a critically important next step in the evolution of the internet that solves many of the issues that cause frustrations today, where it seems that bandwidth alone hasn’t fully enabled reliable and responsive interactive application experiences.
To fully take that step, the segments of the network that are the likely bottlenecks in residential deployments — the access network and the Wi-Fi segment — both need built-in support for L4S.
Wireless
Wi-Fi 7 To Transform the Online User Experience

Wi-Fi continues to be the world’s preferred wireless technology, with a record 19.5 billion devices expected to be in use by the end of this year. Many factors have contributed to the widespread adoption and success of Wi-Fi technology, including its support for mobility and its ubiquity due to operation in unlicensed bands and relatively low-cost deployment.
Over the years, Wi-Fi has evolved to support new applications and innovative use cases as technology has shifted toward digitization. Today, users expect more from their Wi-Fi than ever before at home, in the workplace and at school. As the demand for higher data rates and capacity continues to rise, latency and reliability have become key performance indicators to support applications such as online gaming, video conferencing and augmented reality (AR)/virtual reality (VR).
Wi-Fi is based on amendments to the IEEE 802.11 standard. The IEEE 802.11 amendments regularly introduce new features to deliver higher throughput and capacity, increase spectrum efficiency, and lower latency and power consumption. The most recent Wi-Fi generation, Wi-Fi 6 (based on IEEE 802.11ax), was launched by Wi-Fi Alliance (WFA) in 2018 for operation in the 2.4 and 5 GHz bands, and Wi-Fi 6E was launched in early 2021 for operation on the 6 GHz band. Wi-Fi 6/6E has strong market adoption, and WFA is now preparing the next generation of Wi-Fi — Wi-Fi 7 — to support ever-evolving applications and use cases.
Speed, Capacity, Latency and Reliability
The WFA Wi-Fi 7 certification is based on the IEEE 802.11be amendment called Extremely High Throughput (EHT), which operates on 2.4, 5 and 6 GHz bands. The 802.11be amendment increases throughput due to the larger 320 MHz bandwidth available at 6 GHz and 4K quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM). Devices such as laptops are expected to reach speeds up to 5 Gbps in optimal wireless conditions.
One of the unique key features of 802.11be is the multi-link operation (MLO), which allows for simultaneous connections to different bands. On top of higher throughput due to link aggregation, MLO improves reliability, enhances band steering and load balancing, and reduces latency. Latency-sensitive applications and applications that require more deterministic connectivity are also supported thanks to the stream classification service (SCS) feature. The amendment also addresses spectrum efficiency and interference mitigation thanks to features such as multi-resource units (M-RUs) and preamble puncture.
Wi-Fi 7 is already gaining momentum, and many manufacturers — including original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) — have announced the availability of chipsets and solutions. The Wireless Broadband Alliance (WBA) has just released a report that explores how Wi-Fi 7 will transform the way people worldwide live, work, learn and play. The report is available as a free download from the WBA.
Preparing for the Next Generation of Wi-Fi
While WFA focuses on developing Wi-Fi 7 certification to ensure product interoperability, IEEE 802.11 is initiating the development of the next IEEE 802.11 amendment, known as 802.11bn (likely to be marketed as Wi-Fi 8). It typically takes several years to complete 802.11 amendments, and the finalization of 802.11bn isn’t expected before 2027 or 2028.
IEEE 802.11bn will focus on reliability, including increasing throughput at range, reducing tail latency and supporting seamless/near-seamless roaming/mobility. It will also provide schemes to reduce access point (AP) power consumption as regulators around the globe address customer premises equipment (CPE) power consumption.
How is CableLabs working to support these efforts? As part of our ongoing mission to represent the interests of our members, we take part in many WFA and IEEE 802.11 working groups to shape the future of Wi-Fi.
We also actively participate in the WBA, which fosters collaboration and promotes the development of wireless broadband technologies and services. Together with other industry leaders, we’re working to develop a Wi-Fi infrastructure that can support the development of future technology, meet expanding user needs and deliver great user experiences.
Visit our website to learn how we’re supporting these initiatives in our Wi-Fi Lab.

Wireless
Wi-Fi Alliance Launches Wi-Fi CERTIFIED 6™ Certification Program

Wi-Fi 6 has been around for almost a year, in the news and on the shelves. Tuesday, however, marked a key milestone to the deployment of the next generation of Wi-Fi connectivity; the Wi-Fi Alliance has announced the launch of the Wi-Fi CERTIFIED 6 ™ certification program. Wi-Fi CERTIFIED 6™ provides the assurance that certified devices will interoperate and meet the industry-agreed standard requirements. With more than one billion Wi-Fi 6 chipsets expected to be shipped annually by 2022, interoperability is playing a crucial role to guarantee a proper operation of Wi-Fi networks and a seamless user experience.
Based on the IEEE 802.11ax standard, Wi-Fi 6 enhances the former Wi-Fi generations by delivering greater network capacity, improving performance in congested environments, increasing data rates, and improving power efficiency. IEEE 802.11ax Working Group started work on the next generation of Wi-Fi back in 2014. The former 802.11 standards focused primarily on delivering higher peak and aggregated throughput but with the rapid evolution of the Wi-Fi landscape, new use cases and challenges needed to be addressed. The exponential growth of Wi-Fi connected devices made it critical to focus on actual field conditions. 802.11ax, known as Wi-Fi 6, addresses the congestion and interference issues seen especially in dense deployments, to deliver higher average throughput per user. The targeted deployments include busy airports or train stations, public venues, mobile traffic offload, and apartment complexes. For Cable Operators this can translate to improved efficiency by serving multiple users at a higher average throughput in a residential environment or public hotspots.
Wi-Fi CERTIFIED 6™ key features
Wi-Fi CERTIFIED 6™ certification program includes a series of key features listed below:
- Downlink and uplink Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) where the channel width is split in different sub-channels that allocated to different clients. OFDMA increases the system efficiency while decreasing the latency in dense deployment, making more efficient use of the available spectrum. This allows multiple users to be served simultaneously compared to Wi-Fi 5 and earlier where a single user is served one at a time.
- Downlink Multiple User Multiple Input, Multiple Output (MU-MIMO) increases the system capacity. MU-MIMO was introduced in Wi-Fi 5 and is part of Wi-Fi 6 extends the capability to serve up to 8 users concurrently.
- Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) 1024 increases the peak throughput by 25% in good conditions compared to Wi-Fi 5.
- Transmit beamforming uses several transmit antennas on the access point to focus the signal to then destination station. This enables higher data rates at a longer range.
- Target Wakeup Time (TWT) is based on a scheduler that allows devices to negotiate when and how often they will wake up to send or receive data. TWT improves battery life of devices, a feature required for Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
- Basic Service Set (BSS) coloring allows for devices to recognize if incoming traffic is from an adjacent network, allowing devices to take measures to adapt transmissions to optimize intra-network activity.
Wi-Fi 6 certified devices must also meet 3 prerequisites:
- Wi-Fi CERTIFIED N (Wi-Fi 4) and Wi-Fi CERTIFIED AC (Wi-Fi 5) certifications ensure a backward compatibility with former Wi-Fi standards.
- Wi-Fi CERTIFIED Agile Multiband allows devices to make intelligent access point, band, and channel selection, improving efficiency and consistency on congested wireless networks.
- Wi-Fi CERTIFIED WPA3 improves security standards for authentication, authorization and encryption, resolving some vulnerabilities issues of WPA2 that emerged over the past years.
The Role of Wi-Fi 6 in the 10G Platform
Earlier this year, CableLabs® introduced 10G™, the cable industry’s vision for delivering 10 gigabit networks. The 10G platform includes a collection of technologies enabling 10 Gbps symmetrical speeds, lower latencies, enhanced reliability, and security. In addition to the wired related technologies such as DOCSIS 4.0 and P2P coherent optics, the platform includes a set of wireless technologies as an integral part of the network (e.g. Dual Channel Wi-Fi™ and Low Latency Wi-Fi). With almost half of the Internet traffic initiated from Wi-Fi connected devices, the cable industry is devoted to developing and enhancing wireless networks for a seamless user experience. Wi-Fi 6 increased capacity, lower latency, and higher throughput is supporting the necessary evolution of the wireless technologies to address the 10G roadmap.
Wi-Fi 6 is also addressed by Kyrio™, a subsidiary of CableLabs. Kyrios’s Wi-Fi 6 test setup (based on Otoscope®) provides a lab environment for controlled testing. In addition, the Kyrio test house is equipped with Wi-Fi 6 devices to simulate a real-world experience and characterize Wi-Fi 6 performance in a residential environment.

Wireless
MAC Address Randomization: How User Privacy Impacts Wi-Fi And Internet Service Providers
In the era of mobility, location tracking is a major privacy concern for portable device users. Although a growing number of applications make use of location data, operating systems (OSs) provide the ability to turn off location services provided by the GPS or cellular/Wi-Fi connectivity. Wi-Fi access points, however, can monitor device locations without user consent by means of MAC addresses. As a countermeasure to this privacy threat, OS developers are anonymizing MAC addresses, thereby raising technical concerns among network operators.
Unique MAC Addresses Enable User Privacy Infringement in Wireless Networks
Every Wi-Fi radio has a unique 48-bit identifier called a MAC address that is assigned by the manufacturer. The MAC address is a Layer 2 (L2) address used to identify the source (sender) and the destination (receiver) of frames by most 802 network technologies, including Ethernet, Bluetooth and Wi-Fi.
Back in 2013, the privacy implications of targeted probe requests started to become widely publicized. Several companies were reportedly logging and tracking the addresses of nearby devices in unassociated states. In addition, during the connection to the AP, customers were not notified upfront that their movements would be tracked, and historic location data could be used for marketing purposes or sold to third parties.
MAC Address Randomization Increases Device Anonymity …
In response to these privacy vulnerabilities, most OSs—including Android, iOS, and Windows—began to implement their own variant of MAC address randomization while probing the Wi-Fi network. This probe mode guarantees anonymity until the client gets associated with an AP. IEEE 802.11 also stepped up to specify a similar feature in the IEEE 802.11aq Pre-Association Service Discovery amendment to the 802.11-2016 standard.
More recently, OSs have started to implement the use of MAC address randomization for device association to the network. The address is kept consistent per network (i.e., Service Set Identifier [SSID]), so the user doesn’t have to authenticate each time it connects to the same SSID. This feature was added to Android P for experimental purposes, whereas Android Q randomizes the MAC address by default, with per-network customization. Windows 10 implements a similar scheme, while iOS 12 supports the probe mode only.
… But Raises Concerns Over Networking Equipment and Services
Although MAC address randomization is evidently a major step toward user privacy, it can have a wide range of repercussions impacting the Wi-Fi network and other related services. The concerns can be classified into two major categories depending on how/where the MAC address is used, the L2 network layer or the system layer.
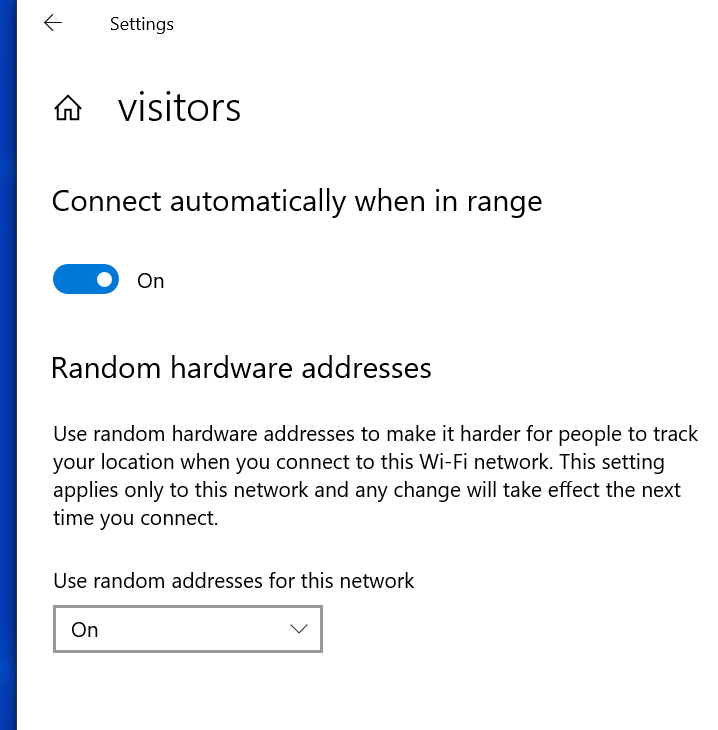
At Layer 2, MAC address randomization can impact network components: One client may be reported multiple times, and networking equipment might be filled up with outdated MAC addresses. Changing MAC address can also negate the effectiveness of some wireless features. For example, band steering and client steering that optimize client connectivity in a multiple AP environment depend on a unique MAC address for probes and association. To address these concerns, IEEE 802.11 recently formed a Random and Changing MAC Addresses (RCMA) group that is assessing the impact of changing MAC addresses on 802.11 features, for both associated and unassociated device states.
Because the MAC address is a Layer 2 identifier, its usage was not intended for beyond L2 networking. In a recent Liaison Statement to the Wireless Broadband Alliance, the IEEE 802.11 working group “strongly recommends against using any specific MAC address as an identifier for a user or device, outside the scope of the layer 2 communication.” However, due to its ubiquity and, so far, expected uniqueness, the MAC address is widely used for various purposes, such as security, access control and billing. The following are examples of such uses:
- MAC-based access often admits or denies wireless association based on the connecting device’s MAC addresses. This includes authentication methods using the MAC address in lieu of a username and password, Pay Per Use (PPU) passes and short-term complimentary services.
- Some accounting and billing systems use the MAC address as a unique device identifier.
- MAC address filtering is often used to add an extra layer of protection on the network (white/blacklist) and enforce policies such as parental control.
- Monitoring, troubleshooting and analytics of Wi-Fi deployments, including help desks, often rely on MAC addresses as part of the client identity.
- Lawful interception makes use of MAC addresses.
Although no recent public data are available, the use of randomization is expected to increase in the near future as more OSs implement it. The definition of a universal randomization policy would support user privacy while ensuring that Wi-Fi and Internet service providers can take proactive measures to update applications and upgrade networking equipment. This requires the involvement of all stakeholders, including standards bodies, hardware/software manufacturers, service providers and OS developers.
CableLabs is currently addressing this topic in the wireless R&D group. Please contact me if you’re interested in getting involved. To learn more about our work in standards and industry consortia, see our members-only (login required) wireless space.

Wireless
Wireless RF Spectrum Scarcity, What About Light Wave?

The scarcity of unlicensed RF spectrum is a never-ending subject in the wireless industry. The 2.4 and 5 GHz bands, once considered profuse, are now overcrowded and regulators such as the FCC are planning to release 1.2 GHz of bandwidth in the 6 GHz band. Over the last decade, this has fueled a growing interest in Light Communication (LC) technologies that offer the potential of THz of unlicensed spectrum including visible light, near-infrared and near-UV. Standard LEDs are now providing illumination while transmitting data at a high rate, and laser diodes (LDs) can reach ~100 Gbps in point to point communications. The recent introduction of products on the market for internet access and wireless backhauling show that the technology is becoming a reality.
What Is Light Communication?
In light communications, the signal is transmitted by an emitting diode (LED/LD) using Intensity Modulation, where the brightness of the light is modulated at a high frequency, imperceptible to the human eye. At the receiver, a photodiode or a camera image sensor converts the received optical power to an electrical signal using Direct Detection. Dimming is possible but often impacts the performance of the system. Rates of Multi-Gbps have been demonstrated with standard phosphor-coated LEDs (1 Gbps) or RGB LEDs (3 Gbps), using advanced modulation technics such as OFDM. Laser Diodes achieves higher data rate over much longer distances but are not always practical in consumer application due to potential health issue and the quality of laser light for illuminations.
LC offers the advantages of a large, unregulated, license-free spectrum, and is already capable in lab environment of reaching 100 Gbps (near field communication). The technology is particularly adapted to environments where RF communications are restricted or pose health concerns. LC is also considered as more “secure” against hackers since the communication is confined in the cone of light within a well-defined coverage zone. Line of Sight (LOS) is required for most use cases.
LC Applications: From Specialized to Mass Markets
With the technology being quite recent, different industries including lighting, transportation, industrial/manufacturing and telecommunication are evaluating its potential.
Specialized markets include location-based services where illuminations can provide a precise location. “Light beacons” are received by smartphone’s camera (supported by recent cell phone models) and an App provides services to enhanced user experience in retail stores or museum places. The aerospace industry is also considering LC to deliver in-flight entertainment.
Outdoor terrestrial link scenarios are attracting much interest fueled by the need of cost-effective wireless backhauls, especially in the context of 5G (small cells). The laser diode transmission usually operates on the near-infrared spectrum due to lower attenuation levels. The technology is part of the Free Space Optic (FSO) communication family that requires a strict line of sight. Available solutions reach 1 Gbps over up to 300 meters with a good reliability, and speeds up to 10 Gbps are on roadmaps. Over longer distances, however, bad weather conditions, especially fog and dust, can significantly affect the throughput. For this reason, the technology is often complemented with mmWave which is mostly affected by rain.
The mass market opportunity, however, resides in the Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) applications where the technology, referred as Light Fidelity (Li-Fi), can complement or, in some cases, replace Wi-Fi. IEEE 802 has recently added a Light Communication task group (802.11bb) to complement the 802.11 family, recognizing the potential of Li-Fi. The standard specifies a PHY operating in the in 380 nm to 5,000 nm band (visible light, near-infrared, near-UV) targeting data rate from 10 Mbps up to at least 5 Gbps for a single link throughput. The uplink in Li-fi systems is usually based on IR transmission due to power limitation of the mobile devices and potential glare of visible light to the user.
Environments that restrict the use of EMI (Electromagnetic Interference) such as hospital, schools and factories are likely to fuel the industry in the next 5 years. The office/enterprise environment is also well suited for Li-Fi where lighting is ubiquitous and Power Over Ethernet is available and serves as a backhaul. In residential environments, Li-Fi can locally offload traffic in heavily populated apartments where RF interference is the primary concern. All these applications are addressed by the 802.11bb standard, while ITU G.vlc focuses on the residential environment.

Light communication is a promising technology that is still in its infancy. The growing interest in this technology is driven by the availability of a huge unlicensed spectrum not susceptible to RF interferences. As CableLabs continues to focus on developing new and innovative wireless technologies, light communications will definitively stay on the radar.
To stay current with what CableLabs is doing in the wireless space, make sure to subscribe to our blog.




