AI
Empowering Field Operations with Agentic AI

Key Points
- Agentic AI is structured around groups of specialized agents that serve as subject matter experts in their own areas of expertise, capable of addressing field operations tasks using structured decision-making.
- The intelligent, autonomous multi-agent system allows operators to integrate predictive analytics into field operations, lowering their costs, minimizing service disruptions and enhancing the customer experience.
Field operations teams are essential for ensuring the seamless performance of modern networks, including hybrid fiber coax (HFC), fiber and mobile infrastructures. However, as networks grow in complexity, traditional troubleshooting methods — manual workflows, static documentation and reliance on expert technicians — struggle to keep pace.
Enter Agentic AI, a transformative approach that embeds intelligent, autonomous AI-driven agents into field operations. These agents act as subject matter experts (SMEs), each specializing in a specific aspect of network troubleshooting, decision support and workflow optimization. By leveraging this structured, multi-agent AI system, organizations can scale expertise, reduce resolution time and enhance operational efficiency.
The Evolution of AI in Field Operations
From AI Assistants to Structured Agentic AI
While AI-powered virtual assistants have been used to support technicians with knowledge retrieval, they lack structured decision-making capabilities. Agentic AI introduces a multi-agent system where each AI agent specializes in a distinct area of expertise, much like human SMEs within an organization.
These specialist AI agents are grouped together into teams based on their expertise, allowing groups of specialist AI agents to collaboratively solve problems in a shared area of expertise, like human teams within an organization. This multi-agent team approach allows for efficient and accurate decision-making to address field operations tasks.
How Agentic AI Operates as a Team of SMEs
Agentic AI is structured around multiple specialized agents, each performing specific roles within the troubleshooting and network maintenance process. These agents collaborate dynamically, ensuring that every decision is informed by real-time data and domain knowledge.
Key AI agents include:
- Knowledge Retrieval Agent (SME in Network Standards & Best Practices)
- Retrieves industry standards, vendor documentation and best practice guides.
- Cross-references sources such as CableLabs specifications and SCTE standards.
- Telemetry Analysis Agent (SME in Real-Time Network Monitoring)
- Continuously monitors network logs, telemetry data, meter measurements and service degradation patterns.
- Detects anomalies like signal degradation, upstream noise or fiber attenuation.
- Troubleshooting Workflow Agent (SME in Guided Resolutions)
- Generates step-by-step troubleshooting workflows based on real-time conditions.
- Adapts workflows dynamically based on technician feedback and sensor inputs.
- Decision Support Agent (SME in Root Cause Analysis & AI-Driven Recommendations)
- Synthesizes insights from multiple agents to determine the most effective resolution.
- Suggests alternative troubleshooting paths if the initial fix does not resolve the issue.
- Proactive Network Maintenance Agent (SME in Proactive Network Health & Failure Prevention)
- Uses historical patterns and AI-driven models to detect potential failures before they occur.
- Recommends preemptive maintenance to avoid service disruptions.
These agents are combined into agentic teams that are tailored to different areas of expertise, such as impairment types, enabling targeted collaboration and troubleshooting. By structuring AI in this multi-agent, SME-like framework, Agentic AI mirrors the way expert teams collaborate in real-world field operations, ensuring that each aspect of troubleshooting and maintenance is handled with precision.
Agentic AI in Action: Enhancing Field Operations
AI-Driven Troubleshooting for Faster Resolution
With Agentic AI, network troubleshooting shifts from manual trial-and-error approaches to data-driven, AI-guided processes. When a technician encounters an issue, the AI agents work together to provide precise, real-time recommendations.
Example: Resolving Signal Impairments in HFC Networks
- The Telemetry Analysis Agent detects signal impairments from network telemetry.
- The Knowledge Retrieval Agent pulls relevant troubleshooting workflows from specs, standards and vendor manuals.
- The Troubleshooting Workflow Agent generates a guided resolution process, suggesting tests with field meters.
- The Decision Support Agent analyzes technician input and network readings, refining recommendations dynamically.
- If the issue is a recurring fault, the Proactive Maintenance Agent flags it for proactive intervention.
This real-time, multi-agent collaboration ensures that field technicians receive expert-level guidance instantly, reducing mean time to resolution (MTTR) and improving service quality.
Scaling Expertise with AI-Driven SMEs
Transforming Field Training & Knowledge Retention
A major challenge in field operations is scaling knowledge across teams. Traditionally, new technicians rely on classroom training and shadowing experienced engineers. With Agentic AI, expertise is available on demand — every technician, regardless of experience level, can access AI-powered SMEs for troubleshooting guidance.
Key Benefits:
- Faster onboarding: New hires gain instant access to SME-level knowledge, reducing training time.
- Standardized troubleshooting: AI ensures consistent best practices across teams based on SCTE Learning and Development guidelines.
- Knowledge retention: AI continuously learns from past cases, preserving institutional expertise.
By deploying Agentic AI as a structured knowledge system, organizations can scale expertise at unprecedented levels.
Beyond Troubleshooting: AI-Powered Proactive Maintenance
Future Work: Predicting & Preventing Failures Before They Occur
Instead of reacting to service disruptions, Agentic AI enables a shift toward proactive and predictive network maintenance.
- The Predictive Maintenance Agent continuously analyzes historical network performance trends.
- AI identifies early warning signs of network failures, such as cable degradation, fiber attenuation, or RF noise issues.
- The system recommends preemptive maintenance actions, reducing truck rolls and service downtime.
By integrating predictive analytics into field operations, network operators can lower costs, minimize disruptions and improve customer experience.
Network as a Service
Empowering the Future of Network Services Through a Federated NaaS Platform

Key Points
- The Federated Developer Portal provides a unified platform for developers to onboard and manage applications across multiple network operators, simplifying Network as a Service access and enhancing scalability, resilience and trust within the ecosystem.
In a world that increasingly depends on digital connections, network as a service (NaaS) has emerged as a game-changing technology. By making network functionalities available as on-demand services across the ecosystem, NaaS empowers developers to build applications that dynamically leverage network resources without needing deep knowledge of the underlying infrastructure. However, as powerful as NaaS is, the process of onboarding developers to access these services remains complex and often inefficient.
To address these challenges, Charter Communications presented a federated approach — the Federated Developer Portal (FDP) — that CableLabs introduced at SCTE TechExpo 2024. The FDP represents a forward-thinking solution that simplifies NaaS access across multiple network operators. This federated model creates a streamlined, secure and scalable environment that allows application developers and operators to collaborate with ease.
The Current Challenges of NaaS at Scale
Although the NaaS APIs that enable developers to create innovative applications are standardized, the processes of onboarding developers and managing applications are not. Because of the current structure, developers must navigate a patchwork of requirements and systems specific to each operator:
- Per-operator onboarding. Developers are often required to individually register and gain approval with each network operator. This process is labor-intensive, repetitive and vulnerable to delay.
- Decentralized integration requirements. Integrating with APIs on a per-operator basis results in diverse, sometimes incompatible processes, creating technical overhead for developers and delaying time to market.
- Single point of failure in centralized systems. When using a centralized model for managing NaaS access, all governance and management operations flow through one system. This approach increases the risk of single points of failure, which can lead to service interruptions or more impactful security vulnerabilities.
Considering these challenges, a federated solution is ideal — one where application developers can register with a consortium of network operators that interoperate at the governance level to manage application developers, applications and their access without compromising trust within the ecosystem. A federated approach offers a resilient, scalable solution that maintains the autonomy of each network operator while giving developers a unified interface for onboarding and management.
What Is the FDP?
The FDP provides a secure, federated platform where network operators and developers interact seamlessly. With FDP, developers can access NaaS capabilities from multiple operators through a single portal, significantly reducing the complexity of onboarding and integration, as well as enabling industry-wide scale. Behind the scenes, trust is maintained through identities based on public key infrastructure (PKI) and the use of digital signatures.
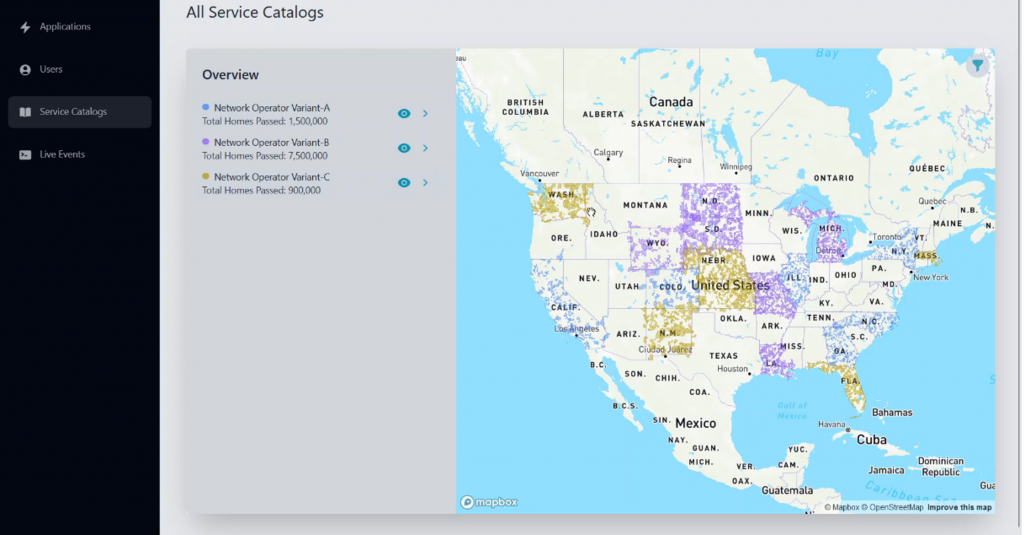
Figure 1: Sample FDP service catalog, from the developer’s perspective
Here are the key features of the FDP:
- Unified interaction point. Network operators and developers have a single, user-friendly interface for application registration, service browsing and management.
- Aggregated service catalogs. Each operator publishes an up-to-date catalog of its available APIs and services, allowing developers to view and select those that suit their applications. This catalog provides essential details, such as API capabilities and supported use cases, giving developers a clear view of network options. Figure 1 provides a sample view of collected service catalogs in our implementation.
- Federated access and approval. Operators retain control over their infrastructure but can securely share service catalogs and API access within the FDP. When developers onboard and submit applications, approval workflows enable each operator to review and approve applications according to its policies, ensuring that only authenticated and authorized applications gain access to network resources.
- Maintained trust. Trust in consortium data is maintained with digital signatures backed by PKI to provide consortium-wide assurance of data integrity and authenticity.
- Modularity. The key components that perform data propagation — the federated agent and the Data Propagation Layer (DPL) — offer an abstraction that enables various propagation technologies, including event streaming, distributed ledgers and more. CableLabs’ key contribution is the definition of governance APIs, which enable flexibility in operator deployment strategy.
An Overview of the Federated Data Portal Architecture
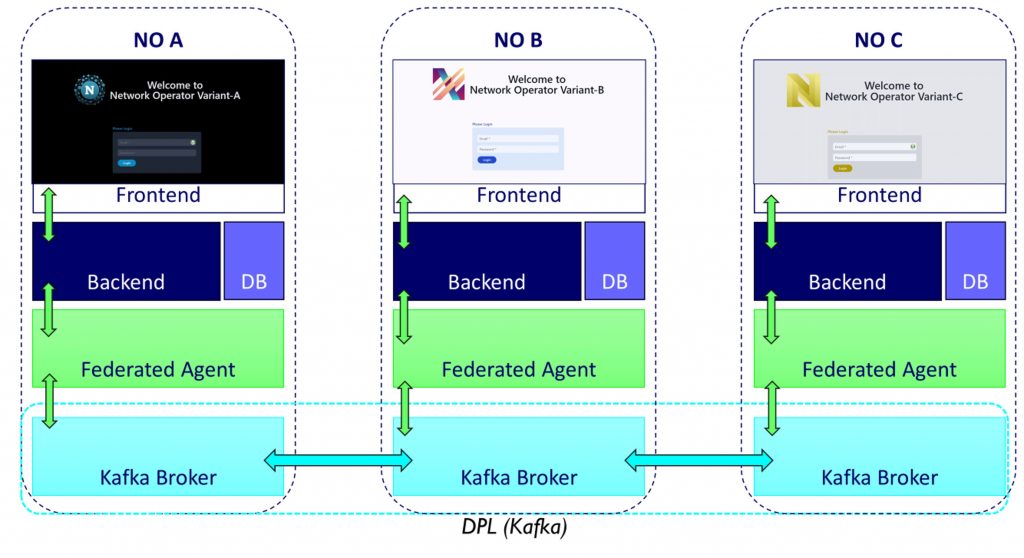
Figure 2 provides a high-level component view of our implementation.
Figure 2: Overview of the FDP architecture
In brief, each network operator deploys a traditional REST API and web interface that application developers can interact with, as well as the components that facilitate data propagation:
- Our DPL is built with Kafka, where governance operations are propagated as events sent to each network operator’s Kafka broker.
- The federated agent is the key element that exposes our governance APIs and enables modularity of the DPL. As the figure shows, the federated agent facilitates propagation by exchanging data with the Kafka layer.
An Example of the Federated Data Flow
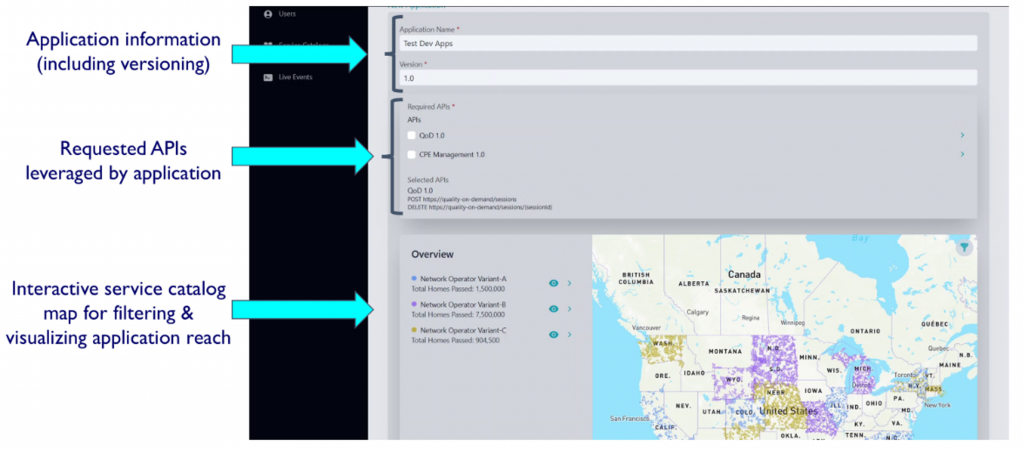
Let’s walk through a high-level example of data propagation through the consortium. Imagine that a developer is registering an application with the consortium of network operators through the FDP, as Figure 3 illustrates.
Figure 3: Sample FDP application submission
- Application submission. The developer submits information about his or her application, including which APIs it will leverage. During this step, the developer can see the reach of that application through an informative display of the aggregated service catalogs that the developer has access to. The figure depicts the application submission form of our FDP implementation.
- Consortium data propagation. The submitted information about the new application is propagated to the other network operators via the federated agent and DPL, ensuring that all network operators receive the updated data.
- Approval flow. All network operators have an opportunity to review and approve the new application when it’s received by their deployment.
Key Benefits of the Federated Developer Portal
By adopting the FDP model, both network operators and developers benefit in multiple ways:
- Reduced complexity for developers. Instead of handling onboarding and API integration separately with each operator, developers interact with a single federated system. This one-stop approach allows them to focus on application innovation rather than logistics management.
- Reduced complexity for operators. Operators establish and maintain relationships with a growing number of developers using a single, consistent process, unlocking the full potential of NaaS at scale.
- Increased resiliency for operators. The FDP’s distributed nature eliminates risks tied to single points of failure. Each operator can maintain autonomous operations, ensuring that system outages or vulnerabilities in one part do not affect the entire ecosystem.
- Distributed centralization. The FDP combines the best of both worlds by providing a centralized interface without compromising the decentralized nature of each operator’s control over its infrastructure.
The Future of the FDP
Although the FDP already addresses key challenges, the platform will continue to evolve. Future iterations aim to support advanced provisioning, offer enhanced metadata within service catalogs and improve governance features for seamless operator and developer collaboration.
Possible enhancements on the horizon include:
- Expanded metadata for service catalogs. Adding more detailed descriptions within catalogs will enable developers to choose services more effectively, considering factors such as network capacity, quality tiers and geographic availability.
- Standardized governance APIs. Establishing uniform governance protocols across operators will streamline approval processes, making it easier to manage applications and handle exceptions.
- Enhanced resiliency and state management. The evolution of FDP will incorporate mechanisms to maintain system stability even under complex operational conditions, ensuring continuous service and data consistency.
Join the Federated NaaS Movement
The FDP is more than just a tool; it’s the backbone for the future of network-driven innovation. With a unified platform, secure data exchanges and a distributed model, the FDP is here to empower developers, simplify operations and strengthen the NaaS ecosystem for all.
All this being said, to fully realize the FDP’s potential, we need input and collaboration from network operators, developers and other stakeholders. Your involvement could shape the future of this platform and help drive innovations that will set new standards for network-enabled applications.
If you’re interested in learning more about the FDP or want to see a live demonstration, don’t hesitate to contact our team! Together, we can build a resilient, innovative foundation that will support the next generation of network-based services.
To learn more about NaaS, register for the next CableLabs Live Webinar, “Taking NaaS APIs to Production: Best Practices and Operational Readiness,” exclusively for employees of CableLabs member companies and our NDA vendor community. The webinar on Dec. 11 will include experts from Charter and Vodafone, who will share insights on how they have been able to expose their APIs to offer differentiated services and take those services into production.
Network as a Service
Quality by Design Streamlines Network Management for Improved User Experience

Key Points
- Quality by Design, a part of CableLabs’ Network as a Service framework, leverages standardized APIs to facilitate communication between applications and the network.
- The specification provides real-time visibility into customer service issues and enables quick resolution.
Service providers and application developers are always striving to deliver the best possible experience for their end users. Optimizing network performance is critical. But in an era of isolated architectures — DOCSIS®️, optical and mobile — traditional network management can be challenging.
In addition, a lack of visibility between applications and the underlying network can make troubleshooting potential network impairments incredibly difficult at an individual user level. The situation is further complicated for application developers, who must navigate varying network conditions and limitations, potentially causing issues that may originate from within the applications themselves.
Recognizing these challenges, CableLabs has introduced Quality by Design (QbD) within the Network as a Service (NaaS) framework. Our goal is to unify and streamline network management.
What is Quality by Design?
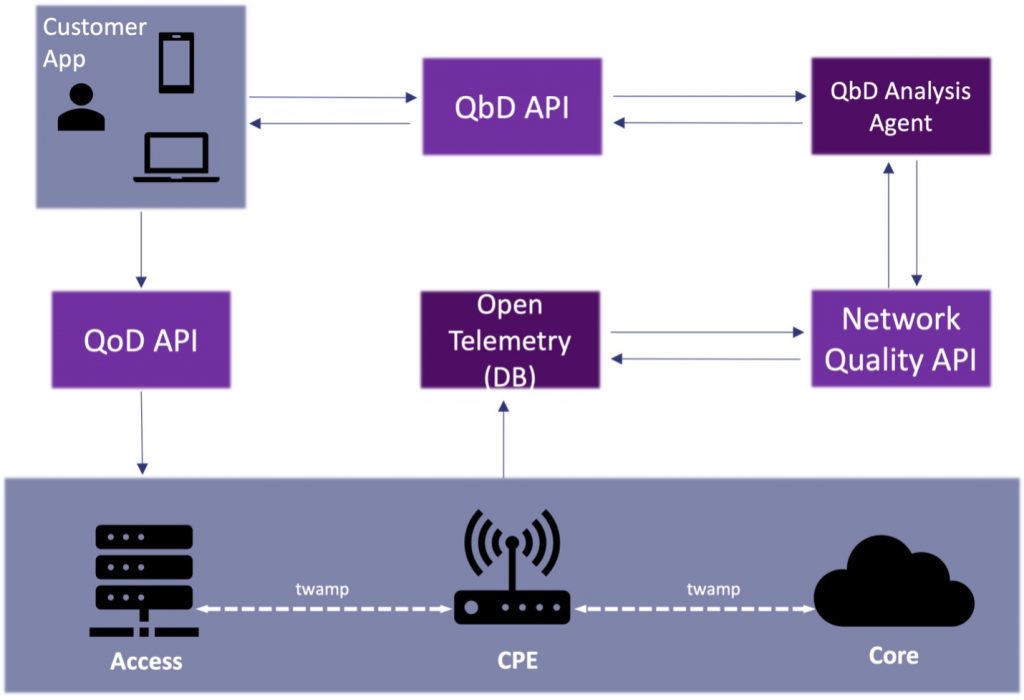
The QbD specification is designed to enhance network performance and user experience through real-time monitoring and automated issue resolution. By leveraging a set of standardized APIs, QbD facilitates two-way communication between applications and the network. Applications can therefore act as network monitoring tools, sharing real-time key performance indicators (KPIs) with the network. Figure 1 shows the QbD design.
Figure 1: QbD Overview
This approach not only provides visibility into user experiences but also enables quick identification and resolution of network issues by correlating application KPIs with network performance data. In this way, QbD swiftly addresses any problems, whether rooted in the network or the application. Customer events are triggered based on a quality score, as Figure 2 shows.
Figure 2: Sample Thresholds for Video Conferencing Applications
QbD enables the swift diagnosis and resolution of network impairments. Automated solutions can then be deployed to address these issues promptly, minimizing disruptions and maintaining high service quality. The inclusion of automated solutions reduces the incidence of excessive network alarms and ensures rapid response to suboptimal application performance.
Impact on End Users
Many factors can lead to end users experiencing degraded quality and suboptimal application performance. QbD helps to address these potential situations by correlating application events with potential underlying network events to determine where the root cause of the problem is occurring through the exchange of KPIs between the application and the network.
This approach allows both applications and networks to dynamically respond to changing conditions, enhancing the customer experience. By turning applications into network quality monitoring agents that actively participate in network management, QbD fosters a more seamless and high-quality user experience.
CableLabs' Role in Quality by Design
CableLabs has been at the forefront of advancing network technologies and standards, and our role in the development and implementation of QbD is a testament to our commitment to innovation. We recognized the limitations of traditional network management, where disparate DOCSIS, optical and mobile networks were often managed on separate platforms with different operations, leading to difficulties in identifying when an individual customer is not getting the level of service they desire.
The QbD APIs have been contributed back to CAMARA, a Linux Foundation Project aligning these intent-based APIs for the broader telco industry. We hope to have the first version published in the near future. This capability transforms applications into proactive participants in network monitoring and management, providing a more granular and accurate view of network performance.
Furthermore, CableLabs has led the charge in integrating automated response mechanisms within the QbD framework. This automation is crucial for reducing the time and effort required to identify and resolve network issues. By leveraging machine learning algorithms and advanced analytics, QbD can correlate application KPIs with network telemetry data, pinpointing potential problems with high precision.
Another key aspect of CableLabs' role in QbD is fostering a collaborative ecosystem among network operators and application developers. By providing a standardized framework and tools, CableLabs encourages these stakeholders to work together, share insights and develop best practices for network and application performance optimization. This collaboration not only enhances the capabilities of individual entities but also contributes to a more robust and resilient overall network infrastructure.
How to Get Engaged
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, ensuring optimal network performance and seamless user experiences becomes increasingly crucial. We invite network operators, application developers and other stakeholders to explore QbD’s transformative potential. Members can request to join our NaaS working group.
By adopting QbD, you can revolutionize your network management practices, deliver unparalleled user experiences and stay ahead in a competitive market.
Visit CableLabs to learn more about how you can implement QbD within your network infrastructure and join the movement toward a more integrated, efficient and responsive digital future. Let's work together to set new standards in network quality and user satisfaction!
Network as a Service
Embracing the Future with Network as a Service (NaaS)

Key Points
- NaaS enables developers to write applications that work across networks and network operators using a single, simple API.
- It streamlines communication and coordination between applications and the underlying network — improving network efficiency and reducing service complexity.
- This approach is more flexible, scalable and user-centric than other current solutions.
In our increasingly connected world, the demand for seamless, fast and efficient online experiences is growing at an unprecedented rate. Imagine a network where your services follow you, enabling an experience that is unique to you — wherever you are, on any device.
This is where Network as a Service (NaaS) steps in, promising to revolutionize the way we interact with the digital world. Let's dive into the what, why and how of NaaS.
Optimizing Online Experiences
In today’s home network, we are simultaneously connecting more devices and running more applications than ever before — all creating the countless online experiences we encounter every day.
What if we could manage these new experiences more efficiently, ensuring that the network is adapting to our needs? That’s precisely the goal NaaS aims to achieve.
By leveraging context awareness, NaaS enables a network that is more responsive to those different devices and applications while giving users a new level of control over their services.
The Impact of Enhancing Connectivity
Improving the underlying network infrastructure isn’t just about eliminating minor inconveniences. It's about unlocking a world of possibilities.
For users, that means an enhanced online experience with faster, more reliable access to services. For operators, it opens up new avenues for revenue through the delivery of new, more advanced network services. Most significantly, it enables a robust, agile network as the foundation for future technologies and experiences in the home and on the go.
NaaS stands at the forefront of this transformation, ensuring that as our digital demands evolve, our networks aren’t just keeping up but leading the way.
What Is Network as a Service?
NaaS is a new approach to networking. It acts as a bridge between the applications we use and the underlying network, allowing for an unprecedented level of communication and coordination.
In simple terms, NaaS lets applications request the network services they need when they need them, thereby ensuring an optimal experience through dynamic network controls. NaaS enables developers to write applications that work across networks and across operators — all through a single, simple API.
This evolved architecture improves the network's efficiency and reduces the complexity of deploying and managing services. Compared with existing solutions, NaaS provides a more flexible, scalable and user-centric approach, heralding a new age of digital connectivity.
A collaboration between CableLabs and Liberty Global, Explorer WiFi leverages NaaS to provide a private network and enhanced Wi-Fi services for guests of hotels and short-term rentals. Video Provided by Liberty Global
The Future of NaaS and CableLabs' Role
The NaaS journey is just beginning. As we look toward the future, we see a digital landscape where networks aren’t just infrastructure but intelligent platforms that adapt to our needs in real time.
CableLabs is committed to leading this transformation, working closely with our members and the vendor community to explore, develop and deploy NaaS solutions. Through working groups, webinars and collaborative projects, we plan to take advantage of the ample opportunities for involvement and stay at the forefront of this network innovation.
Your Invitation to Shape the Future of Networking
Are you excited about the possibilities NaaS offers? Do you want to be part of this digital revolution?
Whether you're a developer, an operator or simply someone passionate about the future of technology, your insights and contributions are valuable. To learn more and find out how you can get involved, click the button below. Together, we can build a more connected, efficient and innovative digital world.
If you’re attending MWC Barcelona 2024, come see NaaS in action. Alongside Liberty Global and Vodafone Ziggo, CableLabs will present a demo illustrating potential applications of NaaS on the fixed network. Look for us in the GSMA booth located in Hall 4, Stand 4F30.
The future of networking isn’t only about faster speeds and more connections; it's about creating a smarter, more responsive infrastructure that anticipates and adapts to our needs. That’s what NaaS is all about.
Join us on this exciting journey!

Virtualization
Crack the NFV Code for Free with our New NFV 101 Training Course

Network Functions Virtualization (NFV), Software-Defined Networking (SDN) and virtualization are transitioning from “buzz words” to reality. As this transition takes place, our members and other players in the ecosystem are asking:
- What is NFV at its core?
- How will it impact my operations?
- What does it mean for my long-term strategy?
In an attempt to answer those questions, CableLabs has developed an NFV 101 training course. This seven-part training series:
- Introduces NFV basics,
- Key NFV requirements,
- Use cases,
- Current industry landscape,
- The role of open source and standards,
- And the future trends we’re expecting from this technology.
NFV will play a key role in shaping how we operate as an industry. With that in mind, this course was designed for anybody who wants to learn more about the technology. Let’s explore in more detail what to expect from each part of the series:
Part 1: NFV Basics
This section will lay the foundational building blocks by exploring what NFV is at its core. You will also find examples of how the technology will impact the network and where SDN plays a role with NFV.
Part 2: Key NFV Requirements
For NFV implementations to be successful, key requirements must be met. This section explores what those requirements are and how to manage those requirements as you encounter them. These key requirements are:
- Cloud-based network topology implementation
- Environmental considerations (e.g., space, power)
- Performance (e.g., latency, throughput)
- Security
- License management
- Availability (e.g., reliability, resilience, fault management)
Part 3: NFV Use Cases
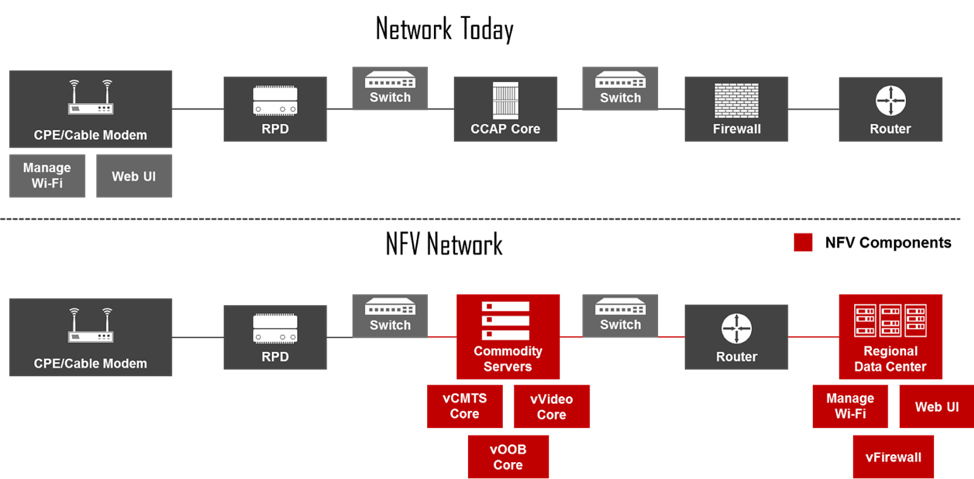
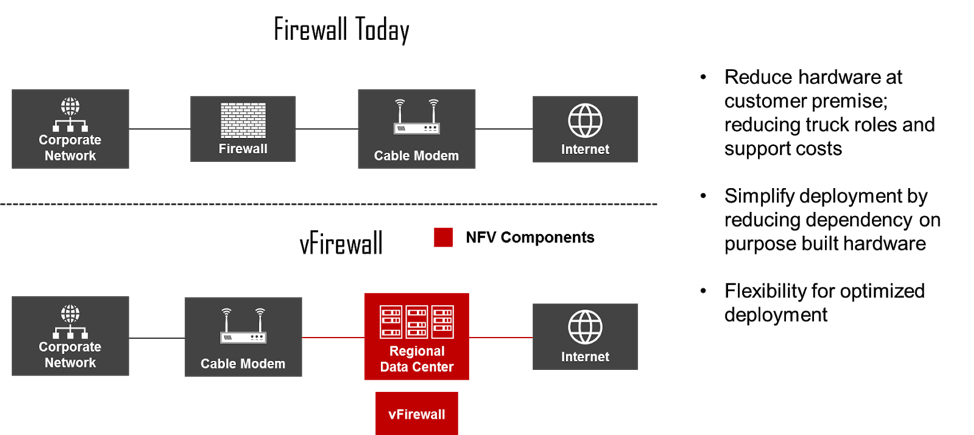
NFV presents some compelling use cases, and in this section, we’ll explore some of the most prominent that we’re seeing in the industry, including vFirewall, vCCAP Core with Remote PHY Device (RPD), and SD-WAN. This section also discusses how each use case will impact your operations and customer base.
Part 4: Industry Landscape
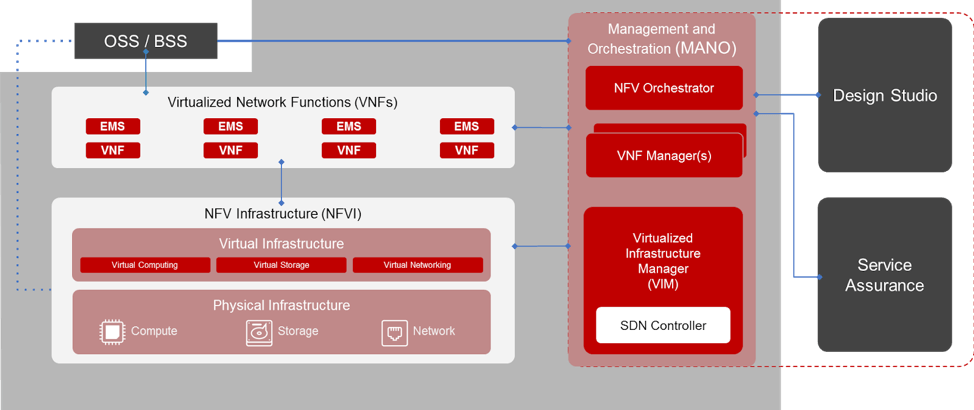
In this section of the training, we will dive more deeply into the NFV architecture and what role each of the major components plays. This section will also highlight what roles network services and Virtual Network Functions (VNFs) play within NFV, along with how ETSI has impacted the development and maturity of this technology.
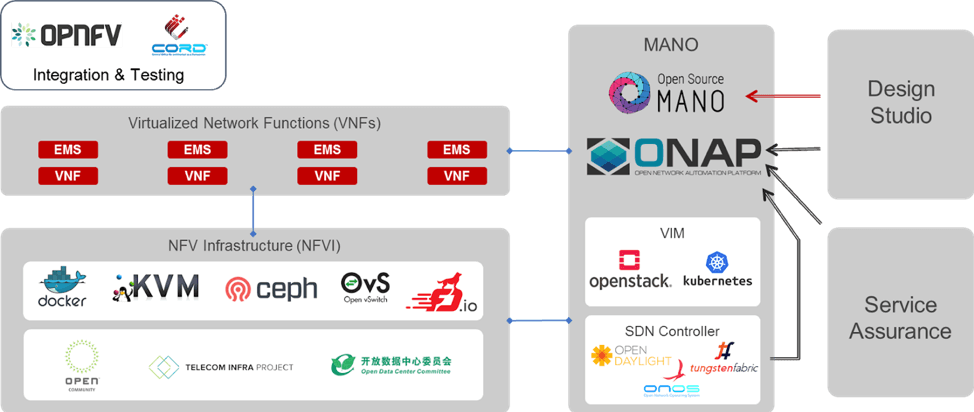
Part 5: Relevant Open-Source Projects
As NFV technology has matured, so have open-source initiatives to improve the technology and interoperability. This section will review the major open-source initiatives and the role they play within the architecture.
Part 6: CableLabs and NFV
As open source and standards mature and shape the future of NFV, CableLabs is playing a key role in helping shape those groups for the entire cable ecosystem. CableLabs has developed a program called SDN & NFV Application Platform and Stack (SNAPS™). SNAPS is the overarching program that provides the foundation for virtualization projects and deployment leveraging SDN and NFV. CableLabs spearheaded the SNAPS project to fill in gaps in the open-source community and to ease the adoption of SDN/NFV for our cable members.
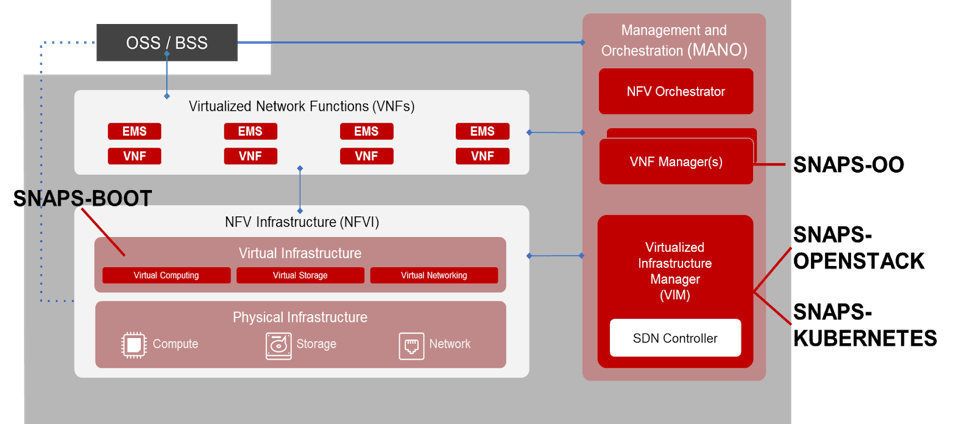
Part 7: Future Trends
Leveraging NFV, cable is poised for the future with the best access network. In this section, we will review where NFV and SDN can take cable networks, along with what to expect from NFV as the technology matures and grows with production implementations.
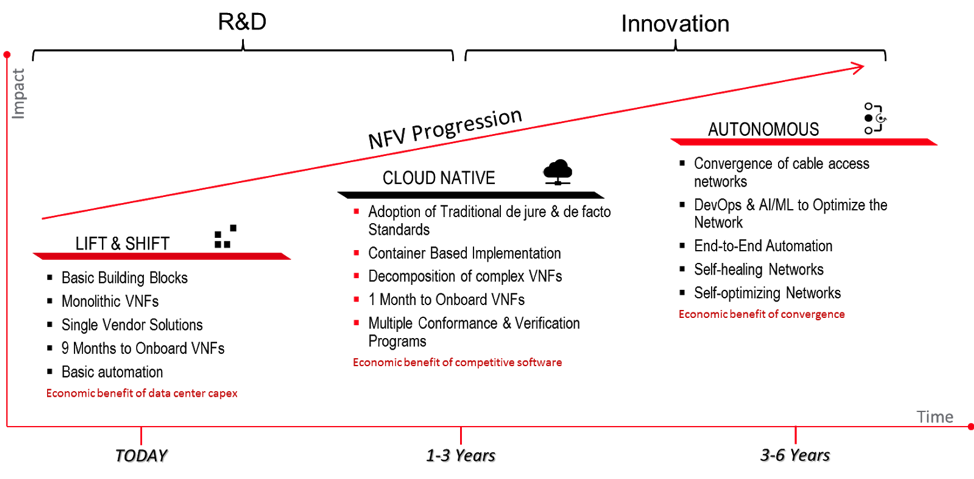
If you have any questions about the content, contact me at p.fonte@cablelabs.com. If you would like to request a live training session of the course, contact Amar Kapadia at akapadia@aarnanetworks.com. To review the video series of the training, click below.